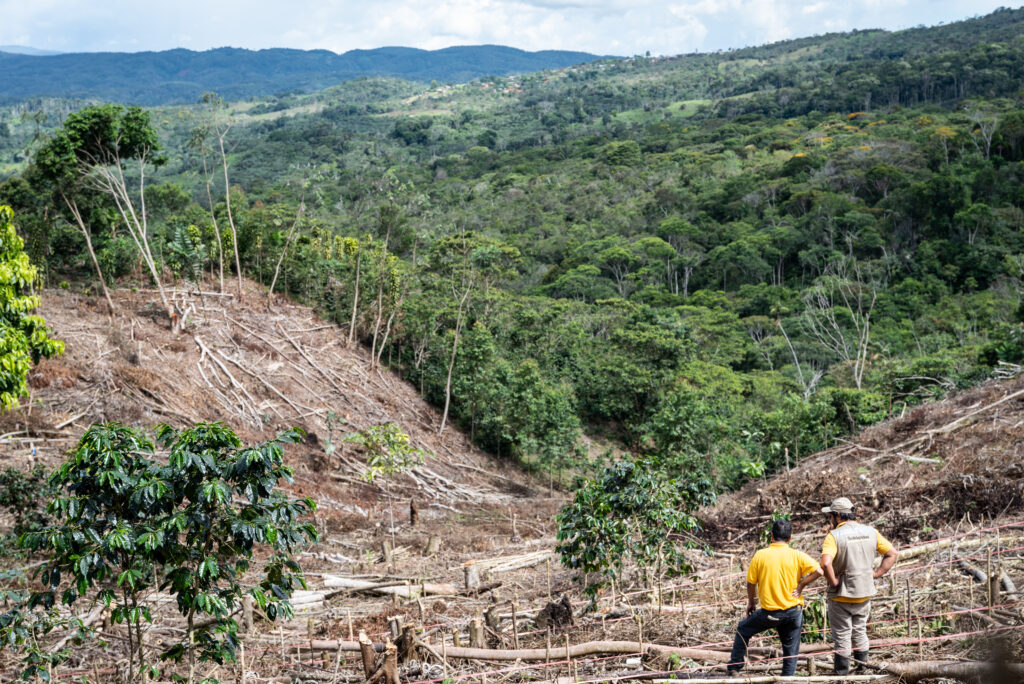
Where We Work
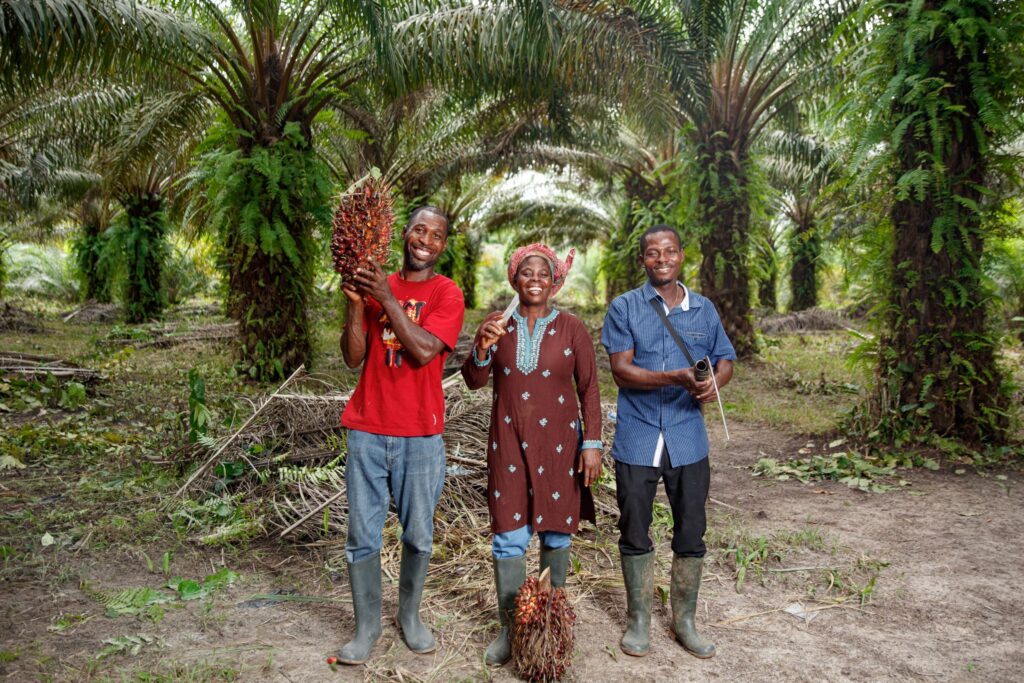
We work across Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Honduras, Guatemala, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname and Uruguay. We have a growing team of experts who develop innovative solutions to improve our partners’ sustainability performance, focusing on nine commodities sectors: coffee, cocoa, fruits and vegetables (bananas and orange), mining, palm oil, soybeans and tea and yerba mate.
Commodities

Challenges
Unsustainable Supply Chains
Structural challenges in supply chains prevent the region and its producers from reaching their full potential in terms of efficiency, competitiveness, inclusivity and environmental protection. By addressing these issues, we contribute to more sustainable production and influence markets.
Solutions
Integrated market solutions
We deliver practical solutions that result in efficient supply chains that optimize present and future resources. Our ambition is that these practical solutions are scaled by others, enabling the transformation of commodity sectors.

Achievements
CONTRIBUTING TO SECTOR TRANSFORMATION
In 2024, we worked with 51 companies to test sustainable solutions that improve product traceability, monitoring and technical assistance for their suppliers and producers. By creating spaces where producer organizations, the private sector and public actors can engage in dialogue, we contribute to sector transformation. Our ultimate goal is to ensure conditions that enable small-scale producers to thrive and steward the lands.
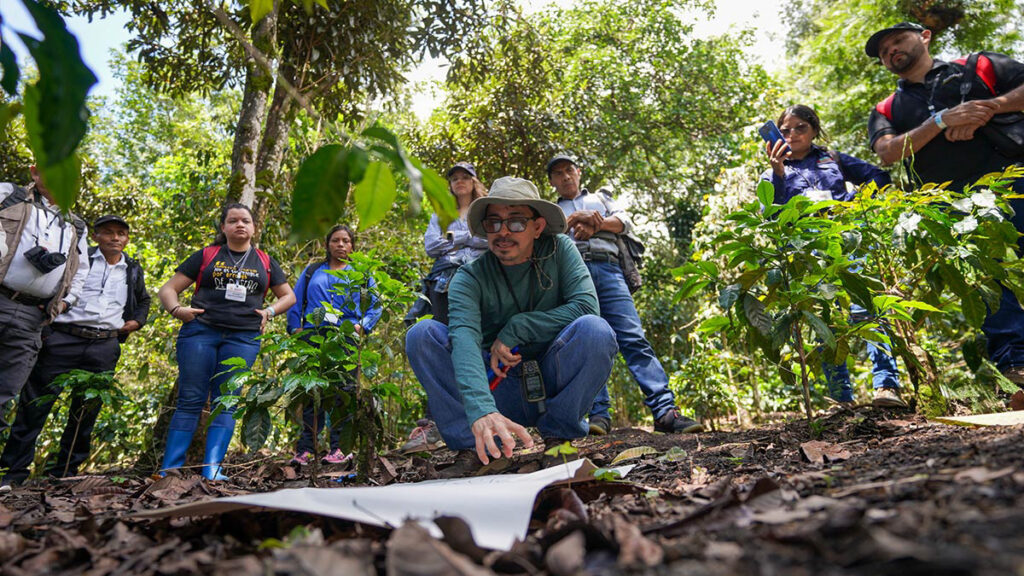

New synergies, more impact
In 2023, we integrated our work in Central and South America to create more impact and synergies. We expanded our climate-smart model with incentives for carbon captures to cocoa, and prepared the groundwork to meet the new EU regulation on deforestation.
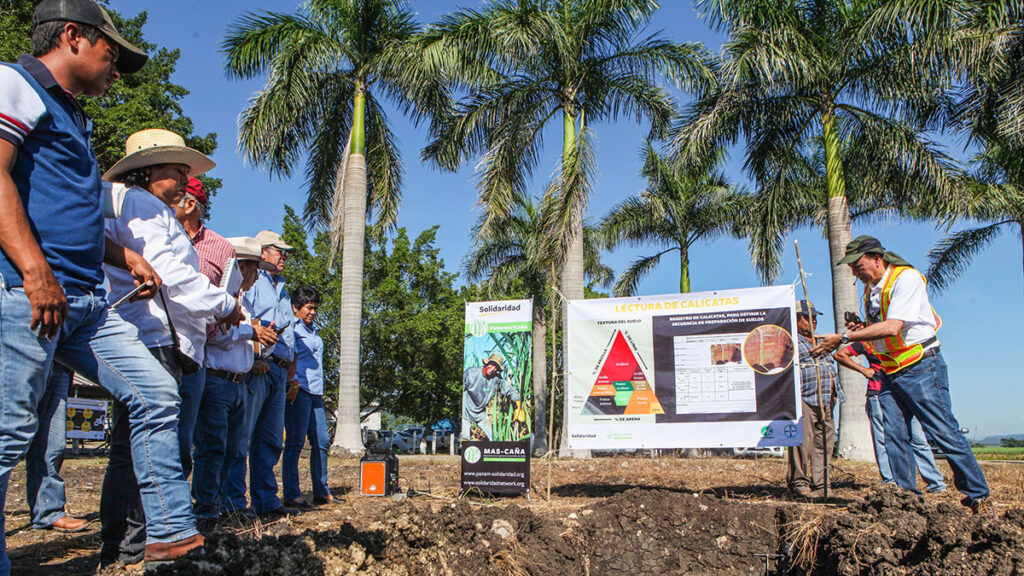

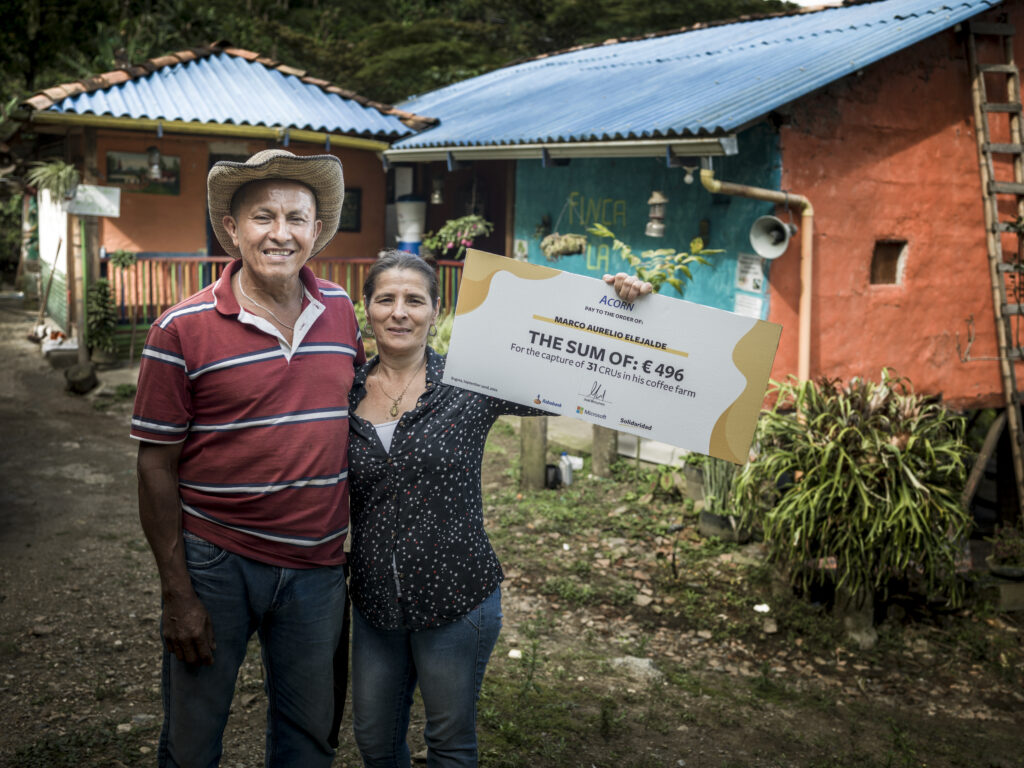
CARBON CREDITS
Carbon credits are becoming an important incentive to introduce smallholders to low-carbon agriculture and protect native forests. In 2022, we secured more than 6M EUR to scale access to the Acorn Platform, through which 80% of the carbon credits’ value returns to the farmer: an interesting proposition within voluntary markets

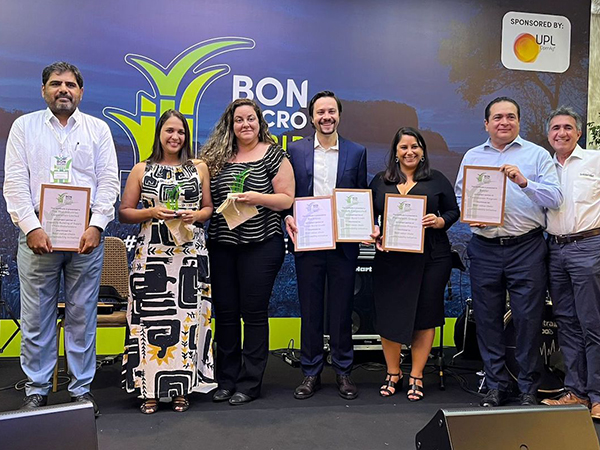
IMPROVED BUSINESS ECOSYSTEMS
Through Muda Cana, in partnership with Orplana, we supported 22 farmers’ associations that have improved their service provision to 6,900 farmers (45 per cent of sugarcane producers in Brazil, the largest producer of sugar in the world). This represents about 45,400,549 tons of sugar cane/year produced on 3,791.73 hectares. MudaCana won the Bonsucro Award for Best value-chain sustainability initiative.

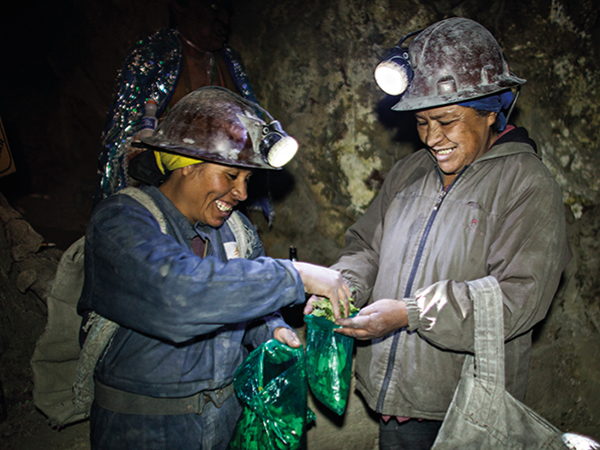
GENDER INCLUSION IN MINING
During three years, the mining programme developed the first gender analysis of the sector in Bolivia, made visible the contribution of small cooperative mining to the country’s economy and consolidated the Women and Mining Network in Bolivia. This action strengthens the leadership and advocacy skills of 200 women, one of whom participated in parliamentary elections.

JURISDICTIONAL APPROACH
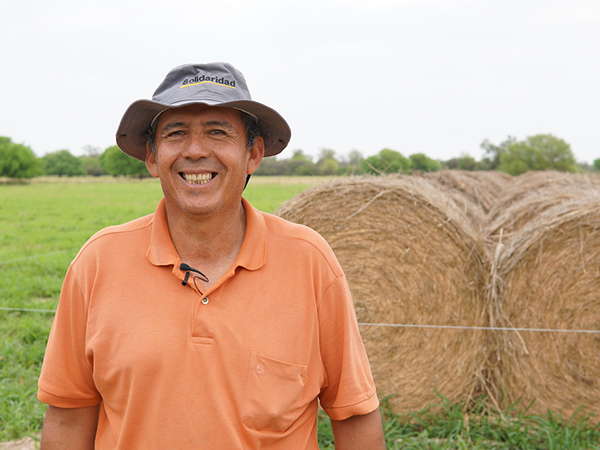
The “Chaco Sustentable” project facilitated the creation of a multi-stakeholder dialogue platform (MSP) where indigenous communities, dairy cooperatives, and government democratically established an agenda of priorities to improve resilience to droughts and other climatic events affecting Teniente Primero Irala Fernández, a district in the Paraguayan Chaco. After four years, cooperatives increased their production by 17 percent and their income by 75%, with 29 percent less GEI emissions per hectare. Indigenous communities built two water reservoirs that can hold up to 36,000m3 of rainfall water for 944 families and grew 136,000 kilos of sesame that was sold to an exporter.

PRODUCTIVE RESTORATION OF THE AMAZON
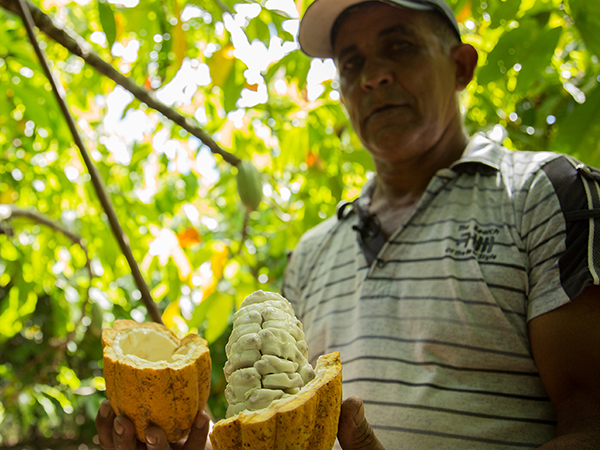
A pilot combined restoration of deforested/degraded land in the Brazilian Amazon (Tuerê) with cocoa under agroforestry systems and livestock intensification practices. After six years, deforested areas decreased by 64 per cent, and GEI emissions decreased by 75 per cent against baseline. Families receiving technical assistance improved their cocoa productivity by 35% and their gross income from cocoa by 51%. The model has proven that for each Real invested in technical assistance, producers gain 4 Reals in income.

CLIMATE-SMART COFFEE
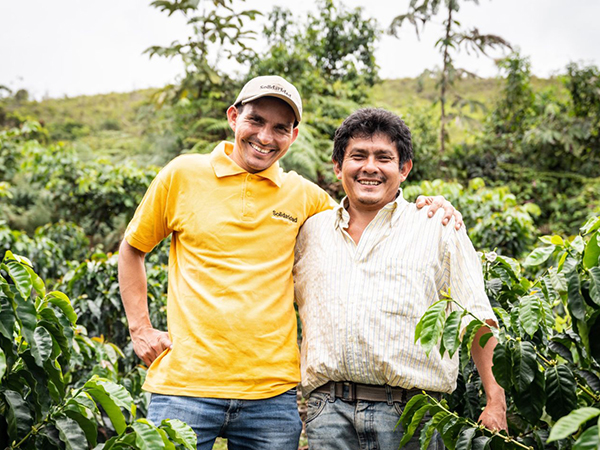
After three years, the first regional pilot of climate-smart agriculture ended having involved 7,361 producers in Colombia, Mexico and Peru who adopted agroforestry systems to grow coffee over 16,000 hectares. As a result, 17,500 tonnes of sustainably produced coffee reach the market and farmer’s productivity increases by 21 percent.

MESOAMERICAN PALM OIL
MAPA opened a dialogue space for the palm oil sector to generate agreements and action plans in Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Mexico. From 2016 to 2022, the initiative managed more than 345,000 hectares under sustainable management, engaging 12,800 producers and 43 processors. It also led to the national interpretation of the RSPO standards in Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua, with 33,200 hectares certified in Honduras and 107,00 in Guatemala.

COMPETITORS CAN COLLABORATE
The Sustainable Trade Platform in Colombia proved that commercial competitors can successfully collaborate on common sustainability challenges. The platform helped to articulate standards, develop climate change adaptation solutions and support producers. In its first four years, the Platform members successfully put in the market 140,165 tonnes of certified/verified coffee, 117,839 tonnes of RSPO certified palm oil, and 38 million boxes of certified bananas.

LEVERAGING SUSTAINABLE SOY PRODUCTION
By engaging with leading companies in the region, Solidaridad and the Sustainable Trade Initiative (IDH) increased the supply of soy produced under several systems of sustainable management by 1.6 million metric tons, covering a total of 845,262 hectares. This confirms that a change of mindset in producers can drive bottom-up market transformation.

Flagship Programmes and Projects
Change that matters with partners who care. Find out what we can achieve together.
NEWS AND RESOURCES
Get in touch
Want to know more about our work in Latin America? Get in touch with our team.
View Larger Map
Contact
Av. Reducto N°1310 oficina 203, Miraflores, Lima 18, Peru
Phone: +51 1 445.4242
infolatam@solidaridadnetwork.org

Gonzalo La Cruz
Managing Director
gonzalo.lacruz@solidaridadnetwork.org

Al Cunningham
Partnership Liaison for Latin America
al@solidaridadnetwork.org

Rosario Abramo
Communications Manager
rosario.abramo@solidaridadnetwork.org

Violaine Laurens
Digital Solutions Unit Manager
violaine.laurens@solidaridadnetwork.org
Continental Supervisory Board

Bernardo Roehrs
President

Roberto Ugaz
Member

Carolina da Costa
Member

María Angélica Matiz
Member